- RoboRuby
- Posts
- Ruby AI News - August 6th, 2025
Ruby AI News - August 6th, 2025
First-class prompt engineering support for Ruby is here

Welcome to (the first part of) the 12th edition of Ruby AI News! This edition features a new prompt engineering solution for Rails, a site tailored specifically for Ruby language LLM benchmarks, RubyLLM shipping updates like crazy, and much more… very soon.
Newsletter update: (Part 2 is now available) This edition is split into two parts. Part 2 comes out tomorrow, and its just as packed with events, career opportunities, and open source updates. It is a lot of content, but this is an awesome problem to have. I’m so excited that there is this much to share. Rubyists are embracing AI and the pace of development in the ecosystem is increasing every week. Keep building and let me know what you’re working on. I’ll try not to make any more two part editions, I think in the fall the newsletter will be an every week release. What do you think? Should I make the newsletter a weekly edition? Did you work on something awesome that I missed? Let me know: [email protected]
Pro tip: Due to the size of the newsletter, many email clients truncate the content. It is recommended to read on the web for the best experience.
Top Stories
New Rails Engine for Managing AI Prompts
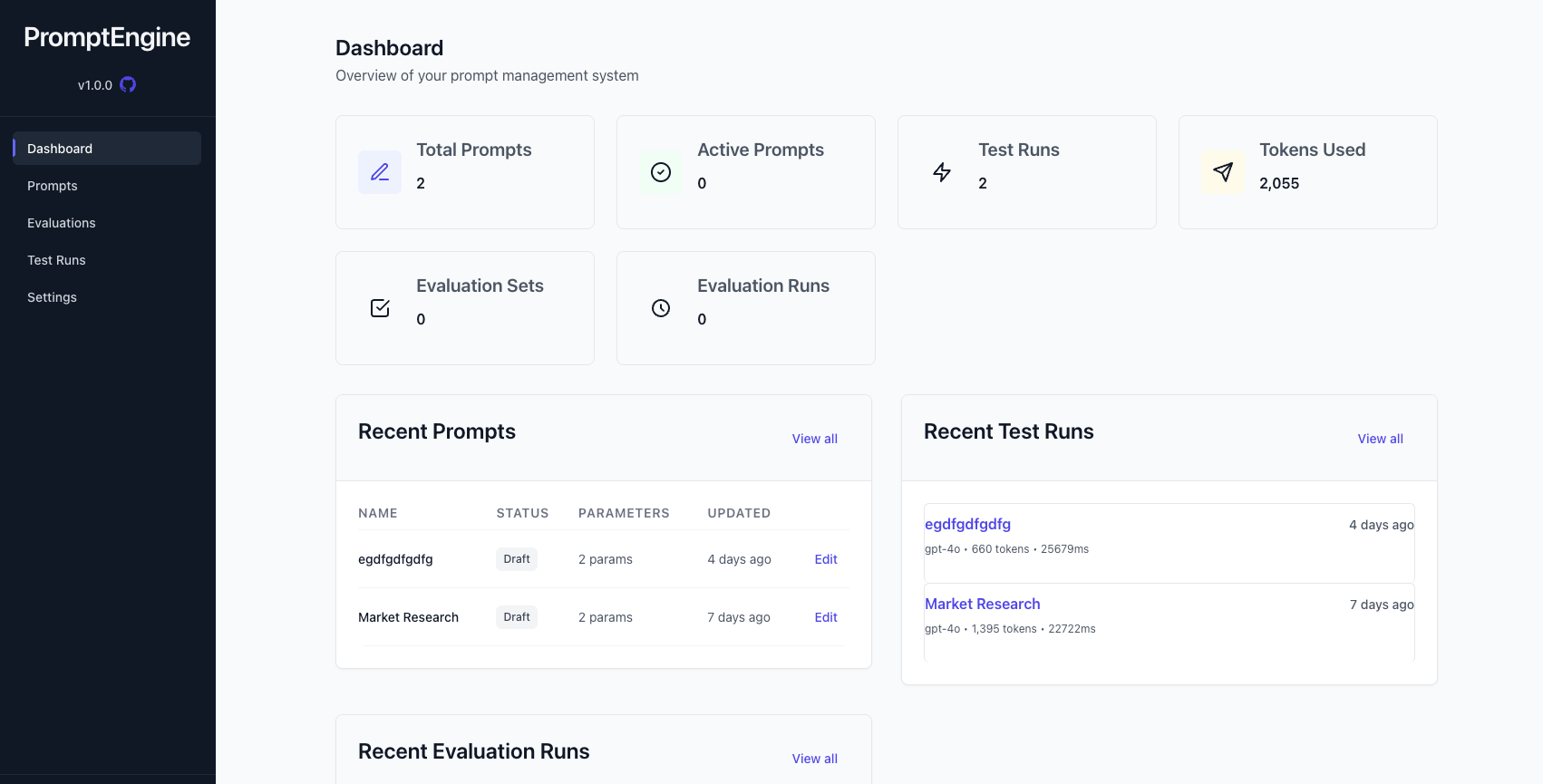
Avi Flombaum introduced PromptEngine, a Rails engine that provides support for prompt versioning, A/B testing, structured schemas, evaluation tools, and seamless LLM integration. PromptEngine allows you to avoid hard-coded prompts by giving you an admin interface to create prompts, store them in a database, and load when you need them. The engine and admin panel bring auditability and pipeline integration to prompt workflows, empowering developers to ship prompt-driven AI systems with confidence.
PromptEngine features centralized prompt management by storing all application prompts in one place with support for versioning. Prompt creation can specify the model, temperature, maximum number of tokens, and the system message, while the prompt itself supports syntax for variables. The admin interface allows you to set LLM provider API keys, work with the prompts, run evaluations, and get valuable statistics on test runs, all with effortless Rails integration. There is already a documentation site, a demo application to test PromptEngine before you install, and the source code is available on Github. Christopher Sonnier is currently working on a new feature for the library to build workflows and chain prompts together where each step's output becomes the next step's input!
I did have some trouble installing the engine from the main branch on Github, as some of the migrations are currently out of order. I created a gist of the consolidated migrations in the correct order you can use in place of the installed migrations if you want to use the latest version of PromptEngine.
Ruby Language LLM Benchmarks
Oskars Ezerins shares a new website showcasing Ruby Large Language Model benchmarks, revealing how different AI models perform on Ruby code tasks. The site highlights comparisons across performance and program-fixing challenges, making model behavior transparent and reproducible. With Ruby LLM benchmarks lacking, it is a valuable resource for developers to assess which LLMs work best for Ruby workflows.
The site showcases performance across two categories: raw performance benchmarks (speed, memory) and program-fixer benchmarks (debugging challenges). Each model follows identical prompts and is measured transparently on metrics like test success, syntax validity, and style compliance. The open-source site uses prompt-based implementation assessments via the RubyLMM gem and OpenRouter models with clear ranking of the models. WIth 46 models tested, Claude 4 Sonnet currently sits as the top model on the leaderboard.
RubyLLM Rocketship
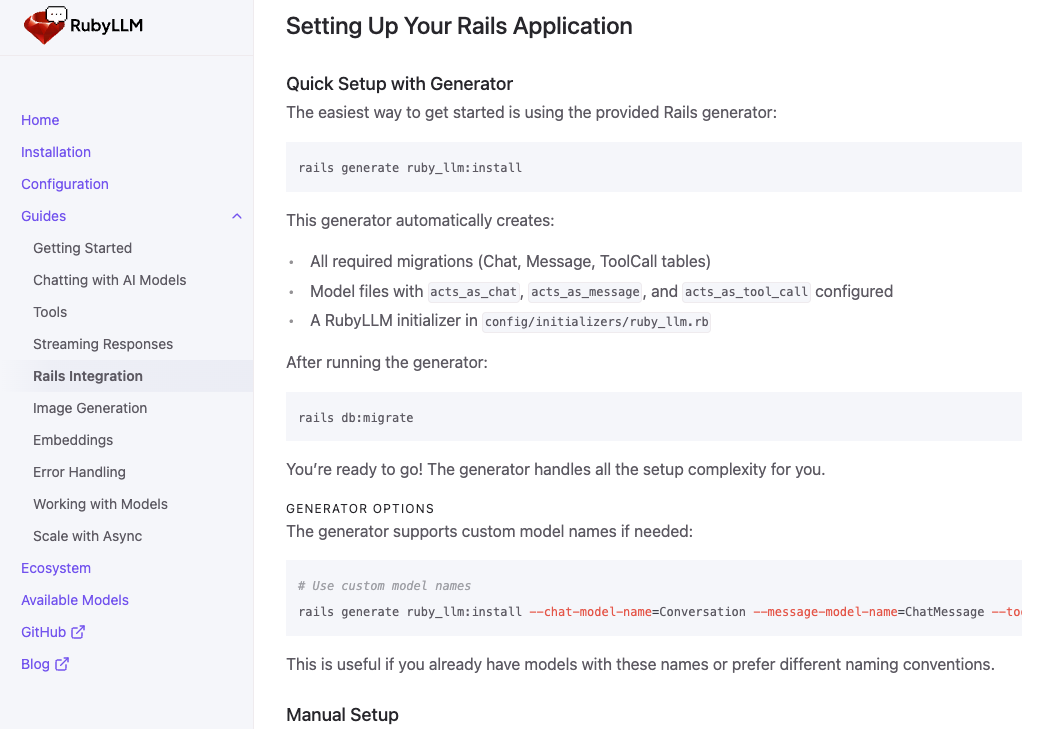
Carmine Paolino shipped a ton of new updates to RubyLLM, a gem for interacting with modern AI LLM models with a clean Ruby DSL. The latest version adds support for 68 new LLM models, including Mistral AI with Pixtral vision and Perplexity for real-time web search. A new Rails generator, rails generate ruby_llm:install, creates everything needed to get started - models, migrations, and the initializer for fast setup. The latest releases also include plain-text Anthropic prompts, improved streaming error handling, tool usage callbacks, and raw response access. Rails integration docs have been expanded at rubyllm.com, and, users are reminded to run RubyLLM.models.refresh! to access the brand-new Claude Opus 4.1 model.
Carmine summarized many of the changes in RubyLLM 1.4-1.5.1: Three Releases in Three Days. He also shared that RubyLLM is used in production by Chatwoot, an open-source customer support tool, and they even built an AI agent framework on top of the library! Another testimonial from Julian Kaiser revealed how swapping out complex JSON schema prompt handling for RubyLLM led to much cleaner code. And did I mention earlier that PromptEngine integrates with RubyLLM for a complete end-to-end AI workflow? Even with all the updates, Carmine still had time to release Cluster Headache Tracker 2.0.
Ken Greeff looked at one of the best new features to come to RubyLLM lately in the video Structured Output Just Landed in RubyLLM (And It's Sick), showing off how to get structured output returned from RubyLLM. Can’t wait to see what everyone’s building with all these new RubyLLM features!
Announcement: Dewayne VanHoozer launched a new documentation site for Ragdoll, an advanced multi-modal document intelligence platform built on ActiveRecord with PostgreSQL and pgvector. Ragdoll is a Ruby gem that provides sophisticated document processing capabilities, leveraging vector embeddings for intelligent document analysis and retrieval. The platform integrates seamlessly with Rails applications through ActiveRecord, making it easy for Ruby developers to add document intelligence features to their projects. The ragdoll source code is available on GitHub.
Tutorial: Amanda Bizzinotto of OmbuLabs explains how to build autonomous AI agents in AI Agents: Implementing the ReAct Pattern in Ruby. The ReAct (Reasoning and Acting) pattern combines large language model reasoning with tool-based actions, allowing agents to think through problems step-by-step while taking concrete actions to gather information or modify their environment. Amanda details building a Ruby implementation that can handle multi-step reasoning tasks, demonstrating how to structure the agent's thought process, action selection, and observation handling.
Article: Vicente Reig demonstrated building AI agents in Rails with the DSPy.rb framework, a Ruby port of Stanford's DSPy for creating structured LLM applications. DSPy.rb brings structured prompting, automatic optimization, and type safety to Ruby developers building AI-powered applications. The DSPy.rb examples repository showcases practical implementations including: prediction, chain of thought, agents with tool calling, mulit-stage pipelines, and data extraction patterns. Over the past two weeks, Vicente has published detailed guides covering the Raw Chat API for Benchmarking and Migration, explained How DSPy.rb Extracts JSON from Every LLM for reliable structured outputs, and showed how to Run LLMs Locally With Ollama And Type Safe Ruby for cost-effective development.
Tutorial: Exequiel Rozas walked through Adding an MCP Server to a Rails App, demoing how to integrate the Model Context Protocol (MCP) into a Rails application. The tutorial shows how to create an MCP server that exposes Rails models and data to AI assistants like Claude, enabling them to read and manipulate application data through structured tools. Exequiel provides step-by-step instructions for setting up the fast-mcp gem, defining tools for database operations, and configuring the connection between Claude Desktop and the Rails app. The implementation allows AI assistants to perform complex queries and data analysis directly on your Rails application's database.
Documentation: Chatwoot launched a new documentation site for AI Agents, a library built on top of RubyLLM for building sophisticated multi-agent AI workflows. AI Agents has powerful features including multi-agent orchestration, agent handoffs, tool integration, callbacks, shared context, and a thread-safe architecture. The docs cover installation, configuration, and examples for building everything from simple chatbots to complex multi-agent systems, with the ai-agents source code available on GitHub.
Tutorial: Wilbur Suero talked through How I Built a RAG System in Rails Using Nomic Embeddings and OpenAI. The tutorial covers setting up document embeddings using Nomic's text-embedding models, storing vectors in a PostgreSQL database with the pgvector extension, and implementing semantic search to find relevant documents. Wilbur demonstrates how to integrate OpenAI's models to generate responses based on retrieved context, creating a complete RAG pipeline that can answer questions about uploaded documents with proper source attribution.
Video: Justin Bowen demonstrated Active Agent in a pairing session with Adrian Marin of AvoHQ. Active Agent (AI Rails Framework) Demo / Pairing - Let's Build Your First Agent in Ruby on Rails! showcases how to build AI-powered Rails applications using Active Agent, a Rails-native framework for building AI features. The demo provides a how-to for structuring prompts, using tool calls, and integrating LLMs.
Announcement: Justin also revealed that Active Agent will introduce structured outputs in version 0.5.0 in this X/Twitter post. The documentation shows that agents will support structured output formats, allowing developers to define schemas for consistent data extraction results.
Article: Leo Trieu of RoR Wizards published Master LLM Performance: Your Complete Guide to Monitoring Token Usage, Latency, and Costs in Ruby on Rails. The article covers monitoring strategies including tracking token consumption, measuring API response times, and calculating operational costs across different LLM providers. Leo provides practical examples for implementing custom monitoring solutions, setting up alerts for cost thresholds, and optimizing performance through techniques like prompt engineering and response caching.
Video: Cezar Halmagean from Mix & Go recorded a video on implementing Rails LLM Monitoring: Track Costs, Latency & Token Usage. The tutorial covers tracking metrics like API costs, response latency, and token usage for AI-powered features, helping optimize performance and manage expenses. The previous video, How to Build an AI Sales Agent With Ruby on Rails, and accompanying sales_agent source code provide a practical implementation that includes monitoring capabilities for an AI sales agent, complete with database schemas for storing conversation data and performance metrics.
Tutorial: Vibe debugging is here! Paweł Urbanek wrote about Using LLMs and MCP to Debug PostgreSQL Performance in Rails. The tutorial introduces rails-pg-extras-mcp, an MCP server that provides access to PostgreSQL diagnostic queries and includes built-in EXPLAIN ANALYZE support for query performance analysis. By connecting this tool to Claude Desktop, developers can interact with their database using natural language queries, automatically generate performance diagnostics, and receive AI-powered insights about slow queries, index usage, and database optimization opportunities.
Video: David Kimura of Drifting Ruby explored the Model Context Protocol, an open standard for connecting AI assistants to external data sources. The episode demonstrates how to implement MCP using Ruby to create a server that provides AI models with access to databases, APIs, and other resources, showing how this protocol bridges the gap between AI models and real-world data. The episode source code is available on GitHub.
Launch: Daniel Rodriguez from LightningRails launched the LightningRails Starter Kit with AI Chatbot Integrations. The starter kit includes pre-built integrations with popular AI services, along with a complete chat interface, message history management, and user authentication. The solution features a responsive chat UI built with Stimulus and Turbo, real-time message streaming, conversation persistence, and role-based access controls, making it easier to add AI chatbot functionality.
Announcement: Chris Petersen released Red Candle - Run LLMs Natively in Ruby with Rust, a Ruby gem that enables running large language models locally without external API dependencies. Built on top of the Candle machine learning framework in Rust, the gem supports GPU acceleration and provides a simple Ruby interface for loading and running popular models like Qwen, Llama, and Phi. The red-candle source code shows examples of text generation and demonstrates how to integrate LLM capabilities directly into applications with just a few lines of code.
Article: Abdelkader Boudih shared The Raw, Frustrating Journey Behind Rails Lens: A Decade of Code Rage, AI Sparks, and Finally Breaking Free. The post introduces Rails Lens, an intelligent model annotations and ERD generation for Rails applications with database-specific adapters, multi-database support, and advanced code analysis that helps LLMs get much better context when working with your application. The rails_lens source code is available on GitHub with installation and annotation instructions. ICYMI, Abdelkader, an amazing contributor to the Ruby AI ecosystem, is having a rough go with AWS, as they recently deleted his account and data without warning.
Opinion: Stan Lo argued that AI Coding Agents Are Removing Programming Language Barriers by making it easier for developers to work across different languages without deep expertise. He demonstrates this with his experience using Cursor AI to work on a Go project despite being primarily a Ruby developer, showing how AI can handle language-specific syntax, conventions, and tooling. Stan suggests this shift means developers can focus more on problem-solving and system design rather than memorizing language specifics, though he notes that understanding fundamental programming concepts remains crucial.
Article: Todd Price of Reinteractive explored how to Supercharge Your Rails AI Chat with Custom Tools, building on his previous tutorial about creating AI chatbots in Rails. Todd demonstrates how to extend basic chat functionality by implementing custom tools that allow AI assistants to perform specific actions like searching databases, making API calls, or executing business logic. The tutorial includes practical examples of building tools for weather lookups and database searches, complete with ActionCable and Turbo Streams for responses and interactivity.
Opinion: Natalie Kaminski from JetRockets argued Why Ruby on Rails is the Best Stack for Vibe Coding in the Age of AI. Natalie emphasizes that Rails' developer happiness and the framework’s magic that handles common patterns makes it ideal for the Vibe Coding and fast-paced experimentation that AI-assisted development enables.
Video: AI on Rails breaks down transitioning from Cursor to Claude Code in Goodbye Cursor, Hello Claude Code? The video examines the differences between these AI-powered coding tools and discusses potential reasons for making the switch from Cursor's AI-assisted development environment to Claude Code’s command line interface.
Opinion: Scott Werner looked at how AI code generation is fundamentally changing the economics of refactoring in Refactoring in the Age of Unlimited Code Generation. Scott argues that when code generation becomes essentially free through AI, the traditional cost-benefit analysis of refactoring shifts dramatically, making it potentially more economical to regenerate code from scratch rather than carefully refactoring existing codebases. In another piece, The Parallel Lives of an AI Engineer, Scott examines how AI tools are creating dual workflows where engineers simultaneously work with both AI-generated and human-written code.
Video: Pete Hawkins of Rapid Ruby released a series of videos exploring advanced Claude coding techniques. The first, You Can 10x Claude Code With These Secret Commands, shows how you can speed up your coding workflow with custom Claude Code commands that handle everything from perfect Git commits to detailed product requirement documents. The second, This Claude Code Workflow Feels Like Cheating, flaunts his supercharged development workflow. The third video, Claude Code Just Took Over My Notes (And It's Unreal), demonstrates a note-taking workflow with Claude Code and Obsidian to help with project development.
Podcast: Valentino Stoll and Joe Leo will host Chad Fowler on the The Ruby AI Podcast on Wednesday, August 6th at 12:30PM EST for Rails After the Robots: Chad Fowler on AI as the Next Abstraction. The panel will discuss treating GenAI as an abstraction rather than magic, covering architecture for machine-written code, designing clear interfaces, and how legacy Rails applications can evolve in an LLM world.
Feedback: Saad Azam shared redlead-cli, a Ruby-based command-line tool that leverages LLMs to analyze business prompts and discover targeted leads from online communities like Reddit. The redlead-cli source code is available on GitHub and Saad is looking for ways to improve the gem.
Announcement: Jeremy Howard released Claude Code Wisdom, a curated collection of coding best practices extracted from conversations with Claude AI. The project compiles insights on software development principles, debugging techniques, code organization, and architectural patterns. The README provides documentation on how to use the collected wisdom, while the full Claude Code Wisdom repository contains the complete collection of insights.
Article: Fernando Martínez of Sinaptia explores Scaling Image Classification with AI. The post details building an image classification system that combines Hugging Face Transformers with Ruby on Rails. Fernando walks through the technical implementation including model selection, API integration, and performance optimization strategies.
Announcement: Nolan Tait released prompt_schema, a Ruby gem that generates BAML-style prompts from dry-schema to get and validate structured responses from LLMs. The library allows developers to define schemas using dry-schema's syntax, then automatically generates prompts that instruct LLMs to return data in the specified format. The prompt_schema source code shows how it integrates with LLM clients and provide validation to ensure responses match the expected schema structure.
Article: Rich Steinmetz introduces his four-part series on Code with LLMs and a PLAN, presenting a structured approach to software development using Large Language Models. The PLAN framework consists of Prepare (setting up the environment and gathering requirements), List (breaking down tasks into manageable chunks), Analyze (reviewing and refining the approach), and Navigate (executing the plan while maintaining flexibility). The series continues with Code with LLMs and Default Instructions, which explores how to create effective system prompts and default instructions that guide LLM behavior throughout development projects. The third installment, Code with LLM Teams, demonstrates how to orchestrate multiple AI agents working together on complex coding tasks, each with specialized roles and responsibilities.
Update: Geir Isene has updated Ruby SHell with direct AI integration. RSH is a Ruby shell designed to replace bash/zsh with a pure Ruby environment, offering tab completion, command history, syntax highlighting, and built-in Ruby evaluation. The latest update allows users to interact with AI models directly from the shell.
Article: Russell Van Curen wrote Build AI Agents in Ruby with Just One Gem to showcase openai-toolable, a gem that handles function calling and execution by including a single module. In the post, Russell demonstrates building a calculator agent and a weather service agent.
Tips: Nate Hopkins shared a 10-step workflow for How to best leverage Claude Code. The approach emphasizes starting with clear requirements and providing appropriate context before asking Claude to propose solutions. Key steps include saving responses to a markdown file with TODOs, iterating line-by-line with explicit references to specific line numbers, and continuously updating the plan as you implement solutions until completion.
Podcast: Victoria Melnikova from Evil Martians interviews Anna Veronika Dorogush: my team makes me proud. Anna is the founder of Recraft AI, an image generation service designed for designers. Anna discusses how their niche positioning as a design-focused tool, rather than a general AI image generator, was a strategic choice that differentiated them in the crowded AI market.
Article: Rakesh Arunachalam of Thoughtbot explores the current landscape of Tools for AI Assisted Software Development, categorizing them into three main areas: code editors with AI capabilities, AI-powered terminals, and specialized development tools. He highlights popular code editors like GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and Windsurf that offer intelligent code completion and chat interfaces, while also covering terminal tools like Warp and Fig that enhance command-line productivity.
Code: Obie Fernandez demonstrated how to run Rubocop with Claude Code hooks, providing an example use case for automatically running linters on every Claude Code update or write operation. The setup gist shows how to configure the hook.
Video: Samuel Williams live streamed Running tests against Agent::Context documentation using Sus::Fixtures::Agent::Context, exploring how to test documentation for agent-based systems. The video showcases using agent-context and sus-fixtures-agent-context to verify that LLMs can understand and apply guidance around thread safety in Async Ruby code. The demonstration coincides with the v0.1.0 release of sus-fixtures-agent-context, which provides a testing framework for validating AI agent contexts. Additionally, Samuel released async-ollama with conversation and tool support, enabling more sophisticated interactions with local LLM models.
Update: Sergio Bayona released VectorMCP v0.3.3, a critical security update for the gem. The release addresses a serious SSE transport session isolation vulnerability that could affect multi-client MCP servers, along with enhanced path traversal protection and improved transport compatibility to resolve race conditions. VectorMCP provides a framework for creating MCP servers that expose tools, resources, and prompts, and users are strongly advised to upgrade immediately to ensure secure operation in multi-client environments. The VectorMCP repository offers documentation and a full changelog.
Article: Jared Norman introduced Order-Driven Development, a methodology that prioritizes the sequence in which code is written and read. By looking at the flow LLM-generated code, Jared argues for structuring code so that dependencies and abstractions are introduced in logical order, making codebases more comprehensible to both new team members and future maintainers.
Update: Alexey Varfolomeev from JetBrains announced RubyMine 2025.2: Junie and AI Assistant Upgrades, Faster Rails Project Startup, Enhanced Bundler Management, and More. The post highlights Junie support for better project-specific context, integration with agentic rule files, and the ability to connect to local AI models. JetBrains AI coding agent Junie also added MCP support.
Feedback: Vinícius Ferreira is looking for feedback for improving the AI Hub gem, a Ruby library that provides a unified interface for accessing multiple AI chat APIs. Features include support for streaming responses, customizable parameters, and provider switching.
Podcast: David Hill and Marty Haught from Ruby Gems Podcast interviewed Even Phoenix in Evan Phoenix: From Rubinius to Ruby Central, exploring his journey from creating the Rubinius Ruby implementation to his current role as Executive Director of Ruby Central. Evan wraps up the conversation with his current ventures and thoughts on the future of tech and AI in coding.
Article: Katie Parrott of Every explores Anthropic's new computer-controlling agents in Vibe Check: Claude's New Agents Are Confusing as Hell - And We Love Them. Katie describes Claude's computer use feature as simultaneously impressive and frustrating, capable of autonomously navigating interfaces but often taking circuitous routes to complete tasks. Still reading the newsletter? Here’s a bit of super secret alpha from Every: while not officially open source yet, the every-cli is available on npm.
Part 2 is available here: