- RoboRuby
- Posts
- Ruby AI News - November 4th, 2025
Ruby AI News - November 4th, 2025
A supersized edition featuring new Ruby AI product launches

Welcome to the 18th edition of Ruby AI News! This editions features awesome AI product launches from the community, a look at Cursor 2.0, and a review of tons of new Ruby AI gems, content, and updates.
Contents
Top Launches
In lieu of Top Stories this edition, I wanted to highlight some of the awesome Ruby AI-related launches I discovered since the last newsletter:
PWV Fund I
Tom Preston-Werner, GitHub co-founder and Jekyll creator, announced PWV Fund 1, raising $100 million for pre-seed and seed stage investments in software and AI-driven companies. The fund operates on three core principles: a founder-centric approach prioritizing founder success through real-world mentorship to accelerate growth and prevent costly mistakes, community building leveraging 150+ active portfolio companies for peer learning and networking opportunities, and strategic connections facilitating warm introductions to top-tier Series A investors. Tom’s 13-year angel investment portfolio includes early-stage bets on Cursor, Stripe, Netlify, Snyk, Supabase, PlanetScale, and Retool in addition to over 175 other startups. The fund is led by Tom alongside partners David Price and David Thyresson, both experienced entrepreneurs with track records building, scaling, and exiting companies. Interested founders can apply at pwv.com/apply.
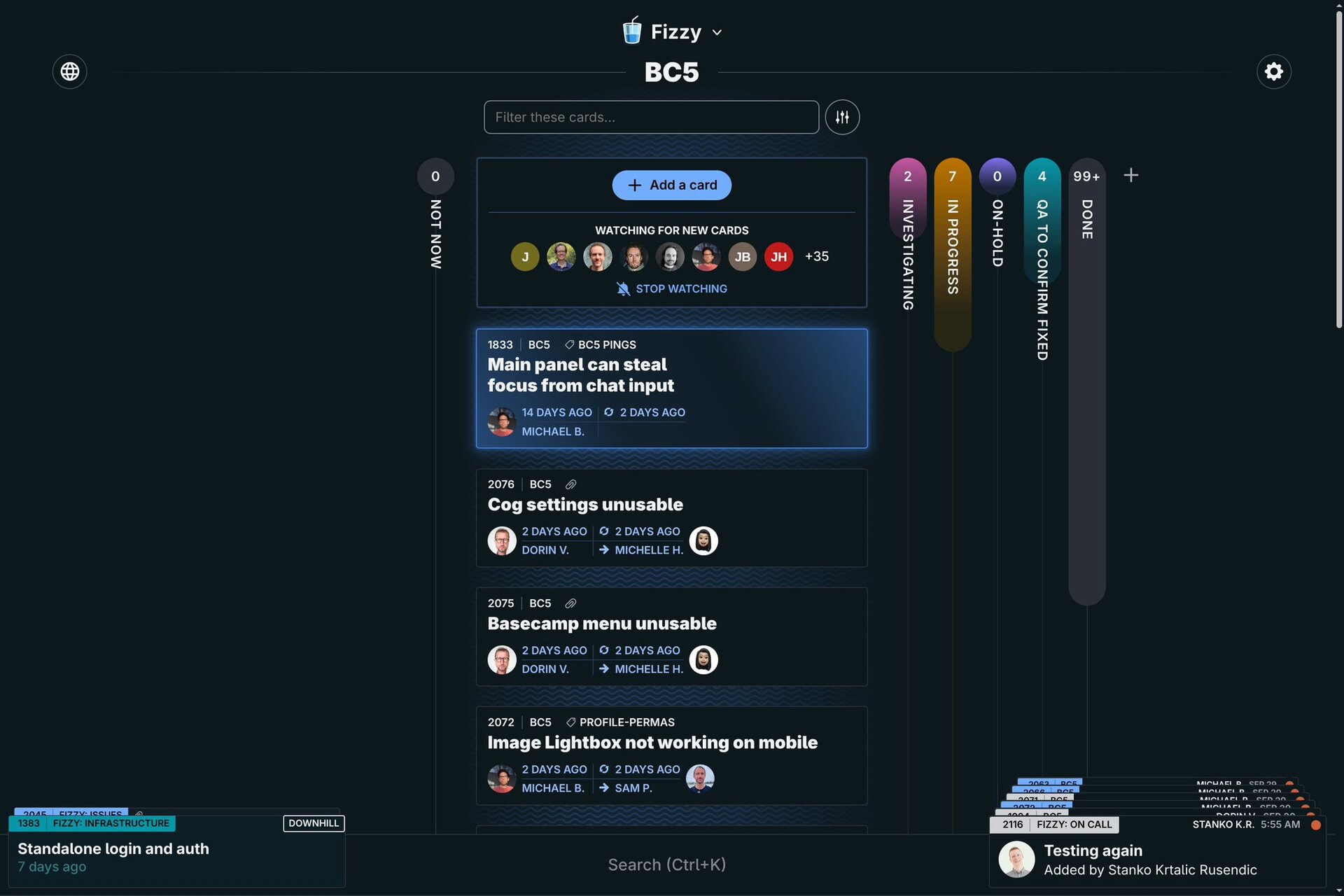
Fizzy
37signals announced Fizzy, a card-based kanban-style issue tracker launching later this year. Jason Fried shared the first preview showing the collection view with cards and two simple columns, designed to be straightforward and approachable for any kind of work beyond software development. David Heinemeier Hansson opened early access signups for a limited number of accounts, describing Fizzy as "our fresh, fun take on cards and kanban-style issue tracking." The product includes a number of Ruby AI features: Jason demonstrated the "Sunday Paper", a weekly AI-generated summary delivered once a week to expose patterns and highlight activity. Jorge Manrubia, Principal Programmer at 37signals, revealed the technical implementation uses Carmine Paolino's RubyLLM gem with the OpenAI API.
Jason and David discussed Fizzy Q's and A's on the REWORK podcast, answering listener questions ahead of Fizzy's launch. They clarified how Fizzy and Basecamp will coexist as complementary tools serving different workflows, showcasing the importance of aesthetic design choices in software products, and provided their perspectives on Fizzy’s AI features.
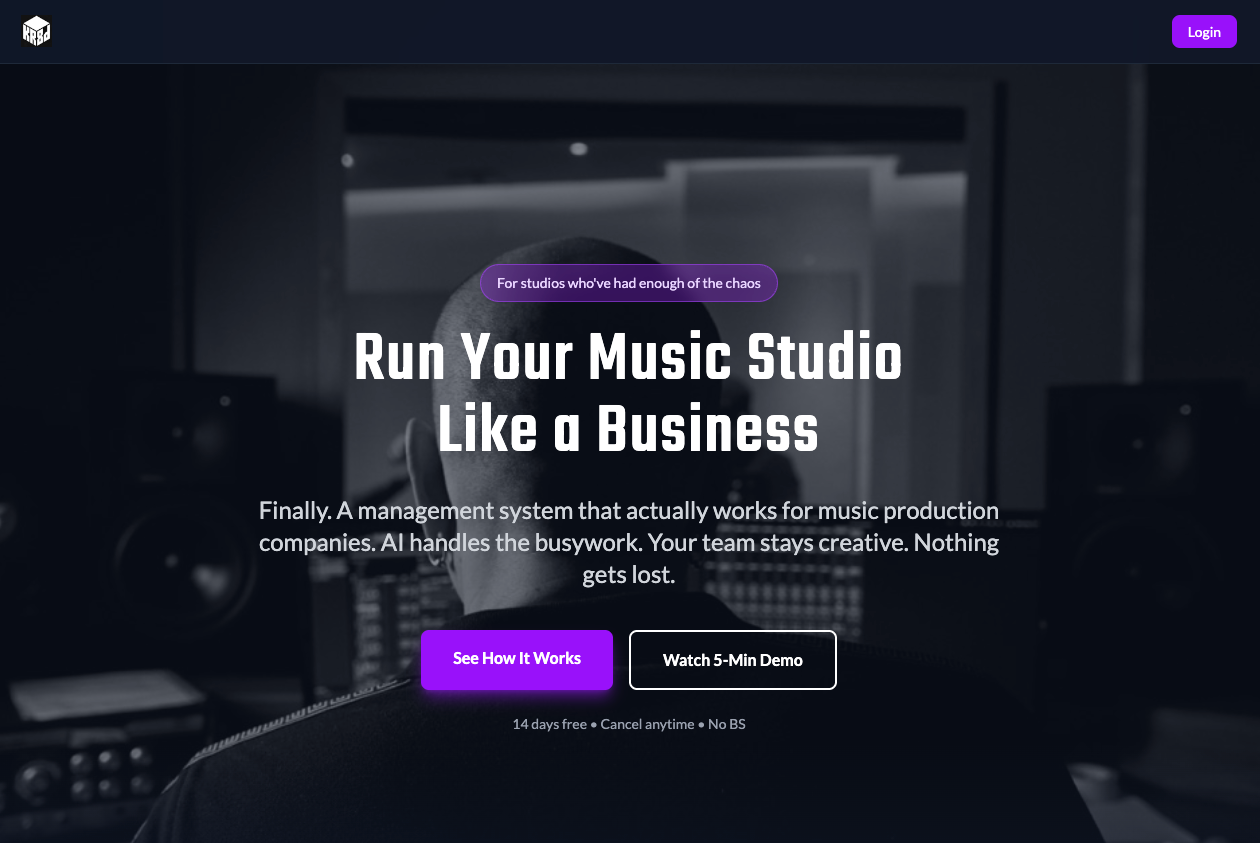
Kr8d
Obie Fernandez revealed Kr8d, a music production studio management SaaS platform addressing pain points in professional studio operations. Kr8d allows you to run your music studio like a business, with AI handling the busywork. The platform automates project organization, version tracking, and workflow management with AI-powered metadata tagging that handles administrative overhead without manual importing. Kr8d features automatic Ableton Live synchronization through a native macOS desktop app, background metadata extraction, waveform preview and version comparison for audio exports, visual workflow boards tracking projects through production stages, centralized team communication reducing email chaos, and automatic versioning of projects, bounces, and masters. Obie shared he built the entire platform solo in his spare time over several months using AI-assisted development, estimating the work would have required a high-end team of 4 developers, 1 designer, and 1 business analyst working 6-12 months, calling it "at least half a mill of wealth creation" and demonstrating the possible productivity gains from AI.
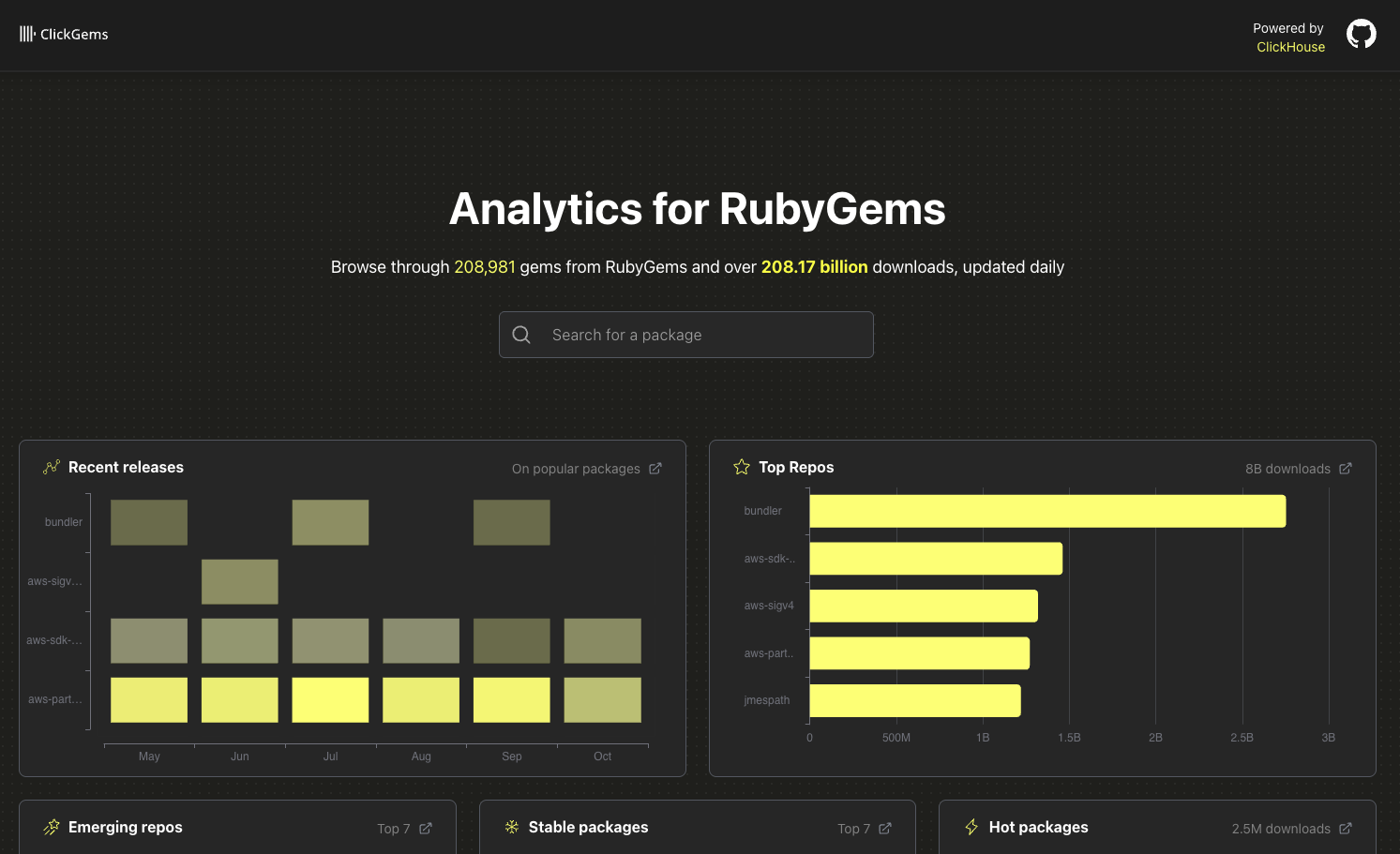
ClickGems
ClickHouse, Ruby Central, and Metabase collaborated to launch ClickGems, a free analytics platform providing comprehensive download statistics for over 200,000 Ruby gems totaling 208 billion downloads from 2017 to present. The platform leverages ClickHouse's analytics database with materialized views for fast query performance, offering shareable charts, download trends, geographic distribution, and emerging package detection across Recent Releases, Top Repositories, Hot Packages, and Stable Packages categories. The ruby_llm dashboard exemplifies the platform's AI-focused gem tracking, showing Carmine Paolino's RubyLLM gem has achieved 3.7 million downloads with significant growth starting June 2025, peaking at over 312,000 downloads in July and September. ClickGems enables developers to export visualizations to documentation and project pages while providing direct SQL query access through ClickHouse's SQL Playground for custom analytics.
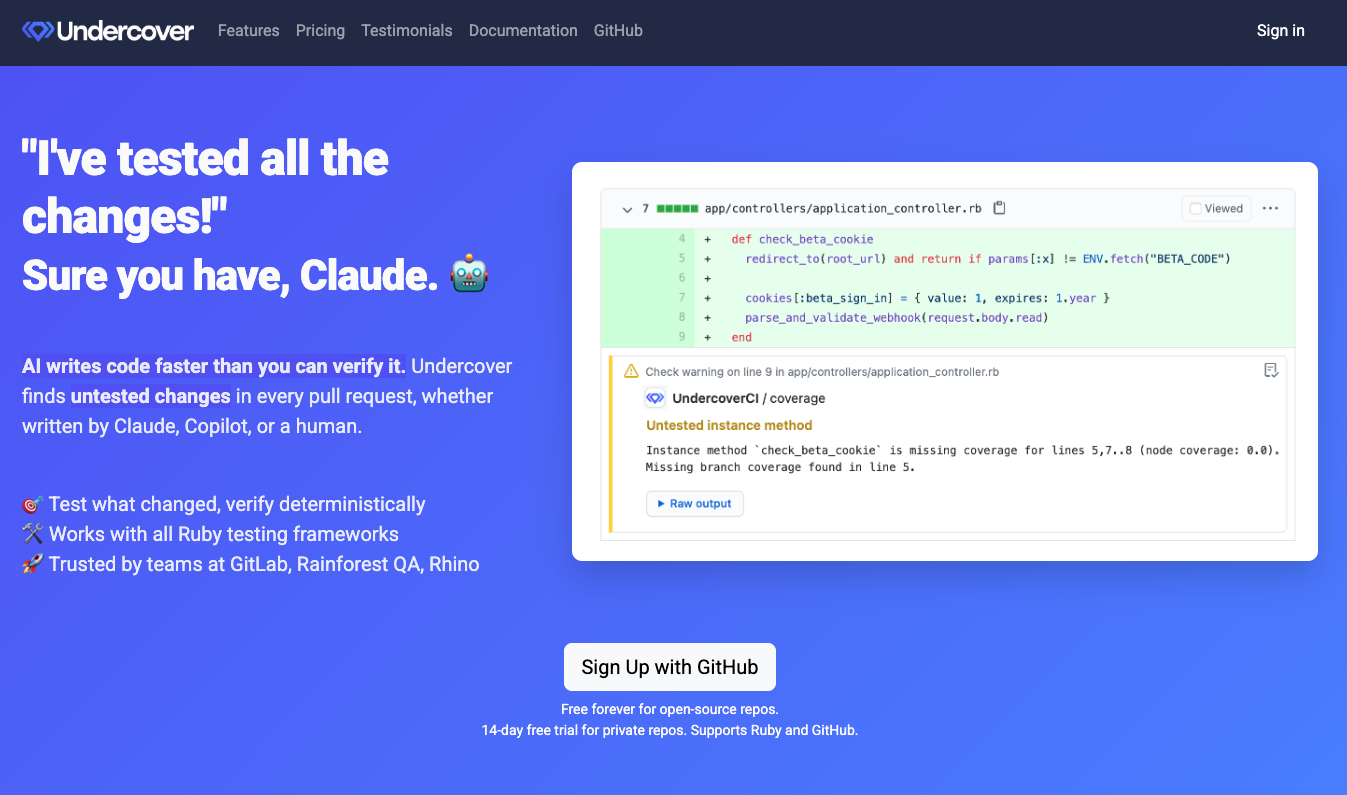
Undercover CI
Jan Grodowski created Undercover CI, a GitHub-integrated service detecting untested changes in pull requests whether code is written by AI tools like Claude or by humans, providing smart annotations and dashboard tracking for PR trends. With a focus on auto-generated code, Undercover CI analyzes code structure and your SimpleCov rules, allowing you to merge commits with confidence and monitor the health of your test suite. Also available as a Ruby gem, Undercover identifies methods, classes, and code blocks modified without test coverage by analyzing git diffs, code structure, and SimpleCov reports. The tool integrates with all Ruby testing frameworks, supporting both line and branch coverage analysis with configurable .undercover files, and runs locally via CLI or in CI/CD pipelines. Discovered thanks to their sponsorship of the Short Ruby Newsletter!
Coolhand Labs
Mike Carroll of Coolhand Labs launched an LLM workflow monitoring platform providing cost and response quality intelligence through a dashboard tracking LLM performance metrics. The platform features quality evaluation loops converting user feedback into automated assessments to prevent regressions, cost optimization with alerts for model switching opportunities and token bloat detection, expense forecasting, and HIPAA compliance for healthcare applications with enterprise-grade security. As part of the launch, Coolhand Labs released coolhand-ruby, a monitoring gem that automatically tracks LLM API calls across multiple LLM models through LLM provider gems that use Faraday. The gem intercepts HTTP calls without requiring code changes, featuring async logging, automatic credential sanitization, and feedback collection.
Orchestry AI
Orchesity created an AI orchestration service for specialized AI agents to generate production-ready backend applications, including Ruby as a supported framework. Built by Rickie Anh Nguyen, the platform moves from prompt to production by generating complete backends with authentication, database integration, tests, Docker, and CI/CD with intelligent task distribution. For Rails developers, Orchesity generates project scaffolding, database integration, secure authentication systems, specialized AI agents, and coordinates AI orchestration with intelligent routing.
Announcement: Cursor, the AI-powered IDE, released Cursor 2.0, featuring Composer, their first proprietary coding model that is 4x faster than similarly intelligent models and completes most tasks in under 30 seconds. The model was trained with codebase-wide semantic search capabilities for enhanced code navigation. The redesigned interface prioritizes multi-agent workflows, supporting parallel agent execution via git worktrees or remote machines, with improved code review mechanisms and native browser integration for automated testing and iteration. Rhea Purohit of Every reviewed Cursor 2.0 and Composer 1 Alpha, examining Cursor's releases of the updated IDE and Composer. Composer's primary strength is exceptional speed that maintains developer flow state for iterative work with clear objectives, though it's less capable than Claude Sonnet 4.5 or GPT-5 for exploratory coding in unfamiliar codebases.
Article: Every's engineering team also documented AI workflows across their six engineers managing four AI products and consulting services. Each engineer customized their stack: Yash Poojary runs Claude Code and Codex on separate machines for parallel comparison and built AgentWatch to monitor multiple sessions; Kieran Klaassen uses Claude Code and three-tier complexity planning for features with Context 7 MCP pulling documentation into prompts; Danny Aziz operates primarily in Droid CLI splitting work between GPT-5 Codex and Anthropic models; Naveen Naidu anchors work in Linear with dual tracks for quick fixes and complex features; Andrey Galko switched from Cursor to Codex crediting GPT-5 for quality UI generation; Nityesh Agarwal uses exclusively Claude Code, interrupting mid-process for explanations to reduce hallucinations. Common patterns include intentional tool selection, planning and context grounding, structured workflows separating execution from exploration, integrated MCPs for design and issue tracking, and asynchronous agent work.
Opinion: Michael Bleigh proposed Context Engineering is Sleeping on the Humble Hyperlink, advocating hyperlinks as an underutilized technique for providing AI models context only when relevant. The approach reimagines HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State) for AI agents that can parse and navigate hyperlinks, requiring minimal scaffolding: a read_resources tool accepting URIs and an entrypoint providing initial URIs. Benefits include easier implementation, token efficiency through on-demand loading, tool consolidation, just-in-time context delivery mitigating recency bias, and flexibility across workflows.
Article: Continuing on this concept, Daniel Doubrovkine wrote about Turning Hypermedia APIs into MCPs, converting HATEOAS APIs into Model Context Protocol servers using a Slack bot as an example. He created the Ruby gem hyperclient-mcp that automates conversion by mapping templated resource patterns directly to MCP concepts, supporting discovery commands to identify available resources and server launch for Claude Code integration. Daniel will be speaking about the hyperclient concept at the ArtificialRuby meetup in December.
Release: Cyril Blaecke released Nosia, a self-hosted Rails and RubyLLM-based RAG platform enabling organizations to run AI models on proprietary data with complete privacy and data sovereignty. The platform provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, vector-based semantic search using pgvector, multi-format document support, and real-time streaming responses via server-sent events.
Update: Carmine Paolino shared recent developments in RubyLLM, including support for Nano Banana with RubyLLM, Google's image generation model that operates through the chat endpoint rather than the typical image API. Just released RubyLLM version 1.9 also adds support for unpacking inline file data from chat responses, enabling developers to retrieve generated images as StringIO objects through a single chat endpoint call. Other updates include a new transcription API supporting OpenAI models with automatic parameter configuration for speaker diarization, plus Google Gemini transcription support. Carmine additionally shipped Anthropic Prompt Caching using raw content blocks for direct access to message content, and introduced a params DSL upgrade with full JSON Schema support via RubyLLM::Schema for defining tool parameters.
Tutorial: JetThoughts published Ruby LangChain Testing Guide | RSpec + Webmock, addressing the challenges of testing LLM applications including non-deterministic responses, expensive API calls, and rate limits. The guide presents a three-layer testing strategy: Unit tests with WebMock and RSpec doubles for free, fast validation; VCR tests recording real API responses once for replay; and gated integration tests against live APIs only on the main branch. Key patterns cover conversation memory testing, error handling for responses with exponential backoff, and CI/CD integration with cost controls including token counting, max_tokens enforcement, and near complete test coverage requirements validated by SimpleCov.
Podcast: Joe Leo and Valentino Stoll of The Ruby AI Podcast interviewed Justin Searls on The TLDR of AI Dev: Real Workflows with Justin Searls, discussing the critical distinction between AI capability and suitability in development workflows. Searls argues that agentic AI tools have entered a "capability spike" where they move faster than established safety mechanisms, creating a gap between what AI can technically do and what's practically trustworthy. The accompanying show notes explores "subtractive vs. generative AI" and advocates for proven agile wisdom applied at a new layer: short loops, real feedback, and stopping when things go wrong, with humans supervising machines rather than just code. Stay tuned for the next episode covering Mastering LLMs with DSPy.rb and Vicente Reig.
Tutorial: Christopher Winslett of Crunchy Data demonstrated Integrating AI Embeddings in Rails using the Neighbor Gem with PostgreSQL's pgvector extension. The gem resolves ActiveRecord's inability to recognize vector data types, enabling proper schema generation including HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World algorithm) indexing, and eliminates the need for raw SQL in migrations. The has_neighbors method provides nearest neighbor queries with euclidean and cosine distance metrics, allowing developers to work with AI embeddings using standard ActiveRecord syntax.
Release: Shannon Skipper ported nanochat to a Ruby gem, bringing Andrej Karpathy's PyTorch language model implementation to the Ruby ecosystem. The gem lets you train and run your own small language models in Ruby, making it possible to build a ChatGPT-style AI that you can customize and fine-tune on your own data. The gem supports model inference, fine-tuning, and tokenizer training.
Update: Vicente Reig released DSPy.rb versions 0.29.0, 0.29.1, 0.30.0, and 0.30.1, bringing architectural changes and prompt optimization capabilities. Key updates include GEPA (Genetic-Pareto Reflective Prompt Evolution) prompt implementation, MIPROv2 (Multiprompt Instruction Proposal Optimizer) enhancements aligning with the Python library, modularization into separate gems (dspy-gepa, dspy-o11y, dspy-o11y-langfuse) for optional dependencies, module-scoped event listeners, and Ruby 3.3 support. Vicente also demonstrated building a production-ready Adverse Drug Event classifier, documented in issue #155 achieving 85% accuracy with 100% recall on clinical text classification. In issue #156, Vicente proposed a Scenic-style versioned migration system for managing optimized prompts as executable Ruby artifacts with git-friendly versioning, integrated metric tracking, and ActiveRecord-like APIs.
Release: Vicente also shared updates on DSPy.rb tooling development across multiple tweets. He is preparing a Deep Search & Deep Research guide for Ruby using DSPy.rb with Shopify's cli-ui gem, exploring Jina AI's architectures alongside Exa AI Labs, with the foundation being metered agents that reason through data before writing. He created the exa-ai-ruby client using a technique of feeding Claude/Codex sample architecture docs with sequence and dependency diagrams, built lf-cli giving AI tools access to Langfuse traces for automating evals, and created whatsapp-cli enabling Codex and Claude Code to interact with WhatsApp.
Article: Anton Kuzmenko of Aha! worked through Streaming AI Responses and Incomplete JSON, addressing the challenge of parsing character-by-character streamed JSON from LLM APIs. Existing solutions like json-repair use O(n²) complexity, reparsing the entire accumulated string with each chunk, causing excessive lag. Anton's stateful incremental parsing approach maintains parsing state between calls, achieving O(n) performance that processes the same JSON 388 times faster with sub-millisecond latency. The solution is available as the json_completer Ruby gem.
Video: David Kimura implemented Failover Requests in Drifting Ruby episode #534, implementing fault-tolerant API calls using the ruby-openai gem. The tutorial builds an OllamaClient class with an attempt_with_failover method that cycles through multiple Ollama endpoints, using local instances with cloud backup for AI model requests. The implementation handles connection errors like Faraday::ServerError by automatically failing over to the next endpoint, raising an AllEndpointsFailed exception only when all endpoints are exhausted.
Podcast: Reinteractive's Technology for Humans podcast featured three Ruby community leaders discussing AI integration and ecosystem challenges with Errol Schmidt: Ben Curtis, Honeybadger co-founder, emphasized that AI can significantly accelerate software development when used correctly but warned developers against blindly adopting AI tools without assessing utility, stressing the importance of understanding technology behind applications. Henning Koch, Makandra founder and Head of Development, discussed the future of legacy Rails apps through Rails LTS, AI's place in development agencies, and Rails comparisons to other frameworks. Shan Cureton, Ruby Central Executive Director, addressed the RubyGems and Bundler ownership transition to the Ruby Core team, confronting community concerns.
Update: Obie Fernandez released ConciseErrors, a Rails gem providing compact error pages optimized for AI coding agents by swapping out Rails DebugExceptions middleware for a minimalist alternative. The gem addresses the problem of Rails default full-page error UI consuming excessive tokens that unncessarily increase AI context windows. In Notes from a Busy Season, Obie shared his continued AI productivity work, including authoring Patterns of Application Development Using AI. He advocates that Ruby on Rails principles emphasizing sensible defaults and clean boundaries pair effectively with AI coding agents, arguing that individuals using agentic AI can now achieve output comparable to entire teams.
Article: Ravi Prakash wrote Meet Your New Rails Co-Workers: Building AI Agents in Ruby Like a Pro and How to Integrate MCP Servers into a Ruby on Rails App (Medium links), exploring Ruby's AI revolution. The first article introduces autonomous LLM-powered AI agents using the ai-agents gem, enabling Rails apps to move from CRUD operations to systems that can reason, take actions, and collaborate. The second article provides a practical guide for integrating Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers into Rails apps using JSON-over-HTTP/WS for passing context and state between applications and AI agents, emphasizing separation of concerns and interoperability.
Release: Keith Bennett released simplecov-mcp: Code Coverage MCP Server v1.0.0, a gem that exposes SimpleCov test coverage data as an MCP server, CLI, and Ruby library. The gem features staleness detection for outdated coverage files, automatic merging of multi-suite test results (RSpec + Cucumber), and multiple output formats including tables, JSON, and annotated source code.
Tutorial: Darko Gjorgjievski explained Spec-Driven Development: What It Is and How to Get Started with Spec Kit + Kilo Code, a methodology that treats specifications as source of truth rather than code to improve AI agent reliability. The approach addresses "vibe coding" ambiguity through GitHub's open-source Spec Kit toolkit, implementing a four-command workflow: /specify creates feature requirements, /plan defines technical strategy, /tasks generates ordered implementation steps, and /implement executes changes sequentially with human oversight.
Tutorial: FuturisticAps wrote Rails + AI/ML: Building Smarter Apps with Ruby, demonstrating how to integrate AI capabilities into Rails applications through external APIs and Ruby ML libraries. The tutorial covers building an AI chatbot using the ruby-openai gem with step-by-step implementation from configuration to frontend, connecting Rails with Python machine learning models via REST endpoints, and performing sentiment analysis with the rumale library.
Article: Islam Gagiev and Joao Gilberto Saraiva of JetRockets described Building a Resilient AI Client in Ruby with Stoplight and RubyLLM, implementing the Circuit Breaker pattern to prevent cascading failures when AI providers experience outages. The implementation uses the stoplight gem to monitor external service calls across three states (Closed, Open, Half-Open), enabling graceful failover from different LLM models while preserving conversation context. The architecture abstracts provider differences through RubyLLM while stoplight handles error isolation, making it suitable for systems requiring uninterrupted AI functionality.
Announcement: Scott Werner introduced touring_test: A Cucumber Extension for AI-Driven Usability Testing, a Ruby gem extending Cucumber to enable AI-driven usability testing that deploys AI agents to interact with websites like real users instead of using hardcoded DOM selectors. The gem currently supports Google's Gemini Computer Use model, taking screenshots and sending them with natural language instructions to the AI which decides actions based on visual interpretation, revealing usability problems that traditional tests with just knowledge of the DOM structure miss. Scott proposes calling this Agentic Behavior Driven Development (ABDD), where agents discover usability gaps and implement fixes until the workflow succeeds.
Video: On Moar AgentBackedCommands: Or How Domain Logic Couples Code, Miles Georgi shared the foobara-agent-backed-command gem, splitting a complex command into two coordinating commands where LLMs operate the domain instead of traditional domain logic implementation. The demo revealed two key insights: code units without domain logic allow interface changes without breaking dependencies that also lack domain logic, and a "deautomation" development pattern where LLMs fill-in domain gaps early, then real domain logic replaces LLM operations later.
Launch: Anthony Panozzo released PlainErrors: Streamlined Rails Error Pages for LLM Agents, a Rack Middleware gem that reduces error page token consumption for AI-assisted debugging. The library’s optimizations enable LLM agents to perform more debugging and iteration within context window limits, particularly beneficial when using tools like Claude Code with the Playwright MCP for local testing.
Podcast: Brendan Buckingham and Ryan Frisch of Rails Business interviewed Scott Werner, CEO of Sublayer, on AI-Driven Development and the Future of Software Engineering, exploring how startups leverage AI tools for development and maintenance. The discussion covered Sublayer's AI products including APM, Augmentations, and the Artificial Ruby meetup. Scott discussed business models for monetizing AI-driven development tools, practical applications in engineering workflows, and how rapid change cycles are creating a "fast fashion era" in software development.
Announcement: Maciej Mensfeld released LLM Docs Builder, an open-source Ruby tool that transforms Markdown documentation for AI consumption, reducing token usage by 85-95% compared to HTML versions. The library strips semantic noise while preserving code syntax and hierarchical context for RAG systems through heading normalization, and generates an llms.txt index file, serving optimized docs to AI crawlers automatically.
Article: Hashrocket added two articles on spec-driven AI development: Vinicius Negrisolo's OpenSpec vs Spec Kit: Choosing the Right AI-Driven Development Workflow for Your Team and Craig Hafer's Spec-Driven Estimation: How Devs Can Estimate Features Quickly and More Accurately with AI. Vinicius compares OpenSpec (faster, simpler for senior developers) with Spec Kit (more structured with explicit role separation), noting OpenSpec moves directly from proposal to implementation while Spec Kit includes detailed task breakdown phases. Craig demonstrates using Spec-Kit's three-step process (/speckit.specify, /speckit.plan, /speckit.tasks) to automate structured thinking that would manually take much longer, generating comprehensive specifications with user stories, test plans, and task dependencies for accurate feature estimation.
Opinion: Drew Breunig argued in Speeds and Swarms that the AI coding community undervalues velocity, contrasting slower models like Claude Sonnet with faster alternatives like Qwen 3 Coder (30x faster), which enables real-time interaction and reduces friction for experimentation. Drew highlights claude-on-rails as an exemplary framework applying Rails' "convention over configuration" philosophy to multi-agent systems, isolating agents to standard Rails directories and pre-loading framework-specific documentation to overcome Git conflict complexity when running multiple AI agents in parallel. He predicts speed will soon take center stage over accuracy benchmarks, creating a paradigm where code emerges nearly as quickly as thought.
Video: Vojtech Rinik recorded Bringing Zod to Ruby on Rails using RubyLLM::Schema, showing how RubyLLM::Schema brings Zod-like schema validation to Rails. The approach validates requests and responses while automatically generating OpenAPI schemas, enabling automatic Swift interface generation for mobile clients. RubyLLM::Schema emulates the TypeScript-first Zod validation library within the Ruby ecosystem, providing type safety and schema-driven development patterns.
Update: Geir Isene announced major upgrades to RSH (Ruby Shell), a single-file Ruby-based shell emphasizing simplicity and extensibility. Recent enhancements include a full plugin architecture, session management, intelligent tab completion weighting based on usage frequency, context-aware learning, command performance statistics, and custom validation rules for dangerous commands.
Article: Kody Kendall documented building an AI coding agent within Leonardo that Writes Rails Tests Using RSpec, choosing RSpec over Minitest after analyzing LLM training data distribution and Rails ecosystem tooling. A key innovation is mutation testing with Mutant, which applies controlled code modifications to verify tests catch actual bugs rather than just achieving coverage percentages, providing objective feedback on AI-generated test quality. The verification stack includes a hardened RSpec configuration, SimpleCov for test coverage thresholds, property-based testing with PropCheck, contract validation via Pact, and RuboCop linting.
Video: Thoughtbot demonstrated AI-assisted prototyping across three livestream sessions: Extreme Rapid Prototyping with Claude where they built an agent to digest research and create a landing page using design-driven prompting, The Dev Side of Claude-Assisted Prototyping where they showed how Claude accelerated development and made live improvements to the prototype in realtime, and Building an MCP-Powered Assistant where the team wired up a lightweight Model Context Protocol server exposing app endpoints and letting the LLM call those tools while keeping responses in a consistent “Thoughtbot voice”.
Launch: Jaye launched a Rails To Revenue series documenting the build-in-public creation of DocForge, a Rails SaaS application developed with AI-assisted workflows. The series begins with the YouTube Intro and Episode 01: DocForge Unleashed outlining the Rails stack supercharged by Claude Code, Gemini, and Codex. Episode 02 covers the Linux Mint dev environment setup on VirtualBox, while Episode 03 demonstrates wiring up PostgreSQL and Devise authentication. The series also includes Creating a Claude Code Agent that automates Git commits by reviewing staged changes, assembling commit messages, and pushing to GitHub.
Article: Shaher Shamroukh detailed Building an AI Social Media Manager with Ruby on Rails: Architecture, Automation, and Lessons Learned, describing RobinReach's service-driven architecture that leverages RubyLLM for AI-powered features including caption and hashtag generation, automated post creation, and content refinement.
Podcast: On the Strictly From Nowhere Podcast, Mike Rispoli, Co-Founder & CTO Cause of a Kind, joined Justin Abrams for Ruby on Rails Is the Holy Grail. They discuss why Ruby on Rails is their preferred framework for software development, and highlight Rails' scalability, strong conventions, portability across deployment options, and built-in features for common patterns. The conversation emphasizes how Rails' conventions particularly benefit AI-driven software development and compares it with Django and Laravel, noting that machine learning applications can be built independently of the web app layer.
Article: Neal Lindsay of Test Double explained Keep Your Coding Agent on Task with Mutation Testing (Javascript-focused), advocating for mutation testing to validate AI-generated code quality. Neal argues that while LLMs excel at code generation, they produce excessive output requiring quality validation, and mutation testing tools like Stryker Mutator deliberately introducing errors to confirm tests actually validate behavior rather than just execute code. Neal discovered the concept through Heckle, an older Ruby mutation testing gem.
Documentation: Playbooks and PulseMCP documented the Hatchbox MCP Server, a JavaScript-based MCP server enabling AI assistants to manage Hatchbox's Rails application hosting platform directly. The server provides environment variable management via SSH access, and controls to trigger new deployments for Rails apps.
Article: Brandon Casci detailed Building a Production App with AI: The Boswell Story rebuilding Boswell, a food bank SaaS platform, using Claude Code. Success required explicit domain knowledge documentation, structured workflows with human review gates, and constraint management to prevent AI circumvention. Brandon argues that AI-assisted development requires months of investment to succeed, with successful vibe-coded weekend projects being the rare exception.
Opinion: Sam Saffron argued in Your Vibe Coded Slop PR is Not Welcome that AI coding tools have made code generation cheap but not code review, creating unsustainable pressure on open source maintainers. Sam recommends maintainers protect their time with strict review timeboxes and close low-quality pull requests without guilt, while contributors should avoid sending unreviewed requests and clearly label AI-assisted work.
Article: Aotokitsuruya explored The Potential of Ruby's ri Command for Coding Agents, developing a Ruby Plugin to integrate ri documentation queries as an agent skill for Claude Code. Official package documentation surpasses search engine results and consumes fewer context tokens when verifying standard library usage. To address limitations including inconsistent ri documentation availability and uncertain version compatibility, Aotokitsuruya created an explicit /ruby:info [query] command directing agents to use ri rather than relying on agent discretion.
Announcement: ImageKit released the imagekitio-rails gem for Ruby on Rails integration, providing view helpers ik_image_tag and ik_video_tag that handle URL generation, transformations, and responsive images automatically with Active Storage support. The gem features AI-powered transformations including background removal, image upscaling, and AI drop shadow effects. The Rails integration processes transformations instantly on ImageKit's servers without round-trips, avoiding Active Storage's variant method limitations, while supporting lazy loading, signed URLs for private content, and responsive images.
Update: GitLab released Composite Identity for AI Features, a security mechanism ensuring AI-generated write operations require dual authentication through both a service account and the human user who initiated the request.
Article: Datadog's SDLC Security team described Detecting Malicious Pull Requests with LLMs, introducing BewAIre, an LLM-powered system reviewing nearly tens of thousands of pull requests weekly with >99.3% accuracy and 0.03% false positive rate. The system addresses security challenges from AI-assisted development accelerating code volume by detecting intent-based attacks traditional static analysis misses.
Announcement: Anton Lovchikov of Evil Martians announced that LaunchKit has been ported to bolt.new, enabling developers to customize the devtool landing page template through AI prompts. The integration allows users to adapt the template to their product using natural language instructions on the Bolt platform.
Launch: Amanda Bizzinotto of OmbuLabs introduced AI Readiness & Transformation Assessment for Development Teams, offering a comprehensive four-week assessment and evaluation framework examining current AI tool usage, infrastructure capabilities, team proficiency, and organizational culture.
Tutorial: Visnupriya explored How to Supercharge Your Rails App with MCP Server and Copilot for AI-Driven Translation, building a translation app using the mcp-on-rails template that enables AI assistants to directly interact with Rails application data and actions. The tutorial covers scaffolding resources, testing with MCP Inspector, and configuring VS Code integration, with security recommendations including authentication, rate limiting, and input validation.
Podcast: Jeremy Smith and Jess Brown discussed artificial intelligence on IndieRails Episode 66: The Obligatory AI Episode, covering AI developments and their perspectives as indie Rails developers.
Announcement: Rafael Silva from Discourse announced Discourse MCP Is Here!, a standalone CLI tool enabling AI assistants like Claude to search forums and read topics in real-time. Rather than embedding MCP directly into Discourse's Rails application, the team built a Node CLI that leverages Discourse's REST API and translates it into MCP calls, inheriting API key scopes and rate limits.
Article: Victor Velazquez of MagmaLabs detailed AI HealthTech MVP with Ruby on Rails: Build Quickly and Securely, providing guidance for building secure AI-powered healthcare MVPs while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
Tips: David Alejandro discovered Samuel Williams' agent-context gem, which automatically generates an agents.md file containing AI context from installed gems that provide context metadata in a context/ directory by running bundle exec bake agent:context:install.
Opinion: Ed Frank from Test Double argued in 5 Rules to Avoid the 95% AI Project Failure Rate that MIT research showing 95% of corporate AI pilots fail stems from organizational issues rather than technology limitations. The five non-negotiables are quantifying success through measurable business outcomes, enforcing agile methodologies at the C-suite level, restructuring leadership decision-making away from command-and-control models, transforming organizational workflows before deploying AI, and fixing fundamental data inconsistencies and broken processes.
Release: The Rails core team announced Rails 8.1. Major features include ActiveJob continuations for resuming long-running jobs, structured event reporting for machine-readable event emission, local continuous integration, and native markdown rendering. Scott W. Hill reported that upgrading to Rails 8.1 was straightforward and demonstrated AI-assisted deployment using autonomous agents that handled testing, changelog updates, production deployment, and documentation.
Tips: Obie Fernandez posted Using Claude Code? Learn to Write Skills ASAP, explaining that Claude Code skills have displaced MCP for him entirely, leading to faster agent behavior. The tutorial provides step-by-step instructions to add the Claude Code Plugin marketplace and install example skills. Obie demonstrates creating a Honeybadger API skill by simply telling Claude to create it, which writes the skill, packages it, and provides installation instructions within minutes, making custom skill creation easier than searching for pre-written skills.
Events
Previous
Rocky Mountain Ruby: Anton Tkachov's conference overview and Jarred Dotterer's personal reflection captured Rocky Mountain Ruby 2025's emphasis on thoughtful AI integration and community values. Key AI-focused talks included:
Scott Werner: We Were Voyagers. We Can Voyage Again!
Christine Seeman: Thoughtful AI for the Rubyist
Brandon Weaver: We Who Remember Magic
Ted Tash: Not Another AI Talk
Don Barlow: Tidewave Web Demo
Travis Dockter: Oh my Claude, What Have I Done
ArtificialRuby: The October 15th ArtificialRuby Meetup in New York City featured three speakers and demonstrations:
Steve Brudz: Self‑Healing Tests & Everflame Reports: AI‑Powered QA for Rails
Damani Brown: Giving AI the Keys to Chrome DevTools
Joel De La Cruz: The New York State RAISE Act: The Race For AI Safety Regulation
Upcoming
November 6th - Meetup: Dresden.rb will meet on November 6th in Dresden, Germany and feature a disucssion by Benjamin Deutscher on LLM Coding and its effects on a developers every day work, debating LLM use and how it affects coding style.
November 7th - Conference: RubyWorld Conference 2025 on November 6th and 7th in Matsue, Japan will include four Ruby AI and hardware talks:
Takayuki Yoshioka: Redmine × Generative AI - The Potential of Issues Management
Koichi Ito: Ruby x LLM Ecosystem
Hayao Kimura: Exploring the World of Electronic Engineering with PicoRuby
Hitoshi Hasumi: Why Now Is the Right Time for PicoRuby
November 12th - Meetup: Ruby on Rails Schweiz is gathering on November 12th in Zürich, Switzerland to host Hana Harencarova for Level Up Your Engineering Career with Mentorship, Pairing, and AI. The presentation will discuss how to tap into mentorship, pair programming, and AI to accelerate your skillsket.
November 12 - Meetup: The Tokyo Rubyist Meetup will meet on November 12th in Tokyo, Japan for a demonstration by Justin Bowen on Agent Oriented Programming with Active Agent, an open source framework to help Ruby and Rails developers easily build AI products and features.
November 15th - Workshop: Rails Fever will be hosting another Rails AI event on November 15th (rescheduled from October 18th) in Philadelphia. This interactive session presented by Peter Bailey will explore how AI is reshaping the modern software development lifecycle. Following the presentation covering the landscape of AI-assisted software engineering, there will be a hands-on workshop to build your own AI-enhanced software development automation.
November 19th - Workshop (Paid, $1,000): Every is hosting Claude Code for Beginners, a one-day online workshop teaching beginners how to build and ship an AI app using Claude Code on November 19, 10 a.m. ET–5 p.m. ET. The beginner-friendly course is designed for both developers and non-developers, featuring live instruction with step-by-step walkthroughs, peer breakouts for collaboration, independent building time, and real-time feedback to ship a project.
November 19th - Conference: The San Francisco Ruby Conference on November 19th through the 21st in San Francisco will include an extensive AI program schedule featuring:
Workshop - Justin Bowen: Building Agents with Rails
Presentation - Brandon Weaver: Rails Expertise, Distilled: AI Agents That Get Your Monolith
Presentation - Tia Anderson: Peace, Love, and CRUD: Finding Calm in the Chaos with Ruby, AI, and a Little Garden Magic
Presentation - José Valim: Navigating Programming Language Evolution in the AI Era
Presentation - Paweł Strzałkowski: AI Interface in 5 Minutes - Model Context Protocol on Rails
Presentation - Enrique Carlos Mogollán: The MCP Fog Made Me Do It: A Ruby Inspector's Unexpected Journey
Keynote - Obie Fernandez: Ruby & AI Conversation
Roundtable - Edward Kim & Ryan King: CTO Roundtable
Keynote - Carmine Paolino: RubyLLM: One API, One Person, One Machine for AI
Presentation - Sarah Mei: The Role of Software Design in an AI World
Startup Demos - Featuring AI companies Fin AI, Bolt.new, Stepful, Simple AI, Sixfold AI, Cora Computer, Superconductor
Roundtable - A panel of venture capitalists interested in Ruby and AI-based startups
Keynote - Vladimir Dementyev: AI-powered Developer Tooling for Rails
Evil Martians shared Why We’re Excited About The San Francisco Ruby Conference and announced that the conference is offering scholarships to approximately 30 students, recent graduates, and early-career developers, with the application deadline on November 8th. Scholars receive complimentary tickets covering the full conference experience including Community Day. Late bird tickets for the conference are also still available.
November 21st - Hackathon: As part of the San Francisco Ruby Conference community day, AngelList will be hosting a Ruby Hack Day from 9am to 4pm in San Francisco.
November 21st - Conference: The Tiny Ruby Conf on November 21st in Helsinki, Finland will include two AI-related presentations including:
Hana Harencarova: Level Up Your Engineering Career with Mentorship, Pairing, and AI
Louis Antonopoulos: Unlocking the Rubetta Stones: Translating a Hoard of Ancient Tablets with Ractors and AI
December 3rd - Meetup: ArtificialRuby is hosting a meetup at Betaworks in New York City on December 3rd. If you are interested in presenting at an ArtificialRuby meetup, please fill out this form and let them know. Speakers will include Daniel Doubrovkine and Vicente Reig.
Open Source Updates
Code Spotlight
Evil Martians open-sourced SF Ruby Clouds, an AI-powered Rails application that transforms attendee photos into whimsical cloud characters over San Francisco's skyline for personalized conference invites. Built with Ruby on Rails, Avo, RubyLLM, and Google’s NanoBanana image generation API.
New Gems
Links to the RubyGems page, newest releases are first:
ollama-dsl - DSL for interacting with Ollama LLMs, allowing streaming and structured prompts
imagekitio-rails - ImageKit Rails integration with view helpers and Active Storage support
rails-worktree - Git worktree management for Rails projects
touring_test - Cucumber support gem for using Google's 'computer use' Gemini model
revirow - Ruby client for the Revirow API
grist-grist - Ruby client for the Grist API
x402-payments - Generate x402 payment signatures and links for blockchain micropayments
workbush - Manage git worktrees with automatic file copying and setup commands
huntress - A Ruby wrapper for the Huntress APIs
x402-rails - Rails integration for x402 payment protocol
dspy-deep_research - DeepResearch orchestration for DSPy
dspy-deep_search - DeepSearch primitives for DSPy
nanochat - Ruby port of nanochat, a minimal LLM
google-cloud-hypercompute_cluster - API Client library for the Cluster Director API
toon-ruby - Token-Oriented Object Notation: token-efficient JSON alternative for LLM prompts
swarm_memory - Persistent memory system for SwarmSDK agents
rankvectors - RankVectors API SDK for Ruby
exa-ai-ruby - Exa API client in Ruby
dspy-gepa - GEPA teleprompter integration for DSPy.rb
dspy-o11y - Observability core (spans, context hooks, and telemetry helpers) for DSPy.rb
dspy-o11y-langfuse - Langfuse auto-configuration adapter for DSPy observability
dspy-schema - Sorbet to JSON Schema conversion utilities reused by DSPy.rb
funes - Agentic memory layer and knowledge base CLI
agentbill-sdk - OpenTelemetry-based SDK for tracking AI agent usage and billing
durable_huggingface_hub - Ruby client for HuggingFace Hub
llm_rescuer - Fix the billion-dollar mistake by spending billions on LLM tokens
dspy-code_act - Dynamic code generation agents for DSPy.rb
pdf_ocr - Ruby gem for extracting text from images using OCR
skald - Ruby SDK for Skald API
braintrust - Ruby SDK for Braintrust
ruby_llm-evals - LLM evaluation engine for Rails
concise_errors - Minimal Rails error pages tuned for AI agents and compact debugging
agentbill - OpenTelemetry-based SDK for tracking AI agent usage and billing
dspy-evals - Evaluation utilities for DSPy.rb programs
lf-cli - CLI for Langfuse
coolhand - Intercepts and logs OpenAI API calls
writers_room - Gem for managing a writers room
mcp-auth - OAuth 2.1 authorization for MCP servers
dspy-miprov2 - MIPROv2 optimizer and Bayesian tooling for DSPy.rb
dspy-datasets - Curated datasets and loaders for DSPy.rb
gepa - Gradient-based Exploration and Pareto Agents for DSPy.rb
codex-sdk - Unofficial Ruby SDK for Codex CLI
exa-ai - Ruby client for the Exa.ai API
reducto - Ruby SDK for the Reducto API
ai_error_clip - AI-friendly Rails development error page with one-click copy
New Open Source
Links to the Github repository:
rails-ai - Claude Code AI agents for Rails development
rack-mcp - Provides AI assistants with ruby code execution capabilities within the context of existing running application server
ClearClaim - AI appeal assistant for healthcare denials
Splat - Exception and performance monitoring tool built with MCP integration for AI agents to query production data
rubocop-ai-style - AI-first RuboCop style configuration, focused on machine readability rather than human aesthetics
SlopGuard - AI hallucination detection for package dependencies
Claudy - Useful plugins, agents, skills, tools for Claude Code
Beaker AI - Voice-first AI phone agent platform
Query My Pod - AI-powered podcast search
Dynamic Prompt - Store prompts in Redis instead of conversation history, enabling real-time modifications
SmartSuite MCP Server - Model Context Protocol server for SmartSuite
Pike13 MCP Server - MCP server for Pike13 API integration
RepoReconnoiter - Analyzes GitHub trending repositories using AI to provide developers with context-aware recommendations
Orchestra AI - Cursor background agents orchestrator
Story - Ruby AI story generator
Jobs & Opportunities
Are you an organization searching for an expert Ruby AI developer, or a Rubyist looking for your next development role with AI and would like to beta test a new job matching platform? Please reach out and let me know the type of opportunity you’re pursuing: [email protected]
One Last Thing
Sometimes you encounter a cute cat at a cafe, an emporer penguin at the zoo, or an Australian box jellyfish surfing off the Great Barrier Reef, and you ask yourself, “Can I pet that dawg?” Well, you might be surprised to learn that the answer is not always “Yes!”. The world is sometimes a dangerous place, so stay safe out there, study up, and test your knowledge:
That’s all for this edition! Be sure to reach out if you have any stories, content, jobs, or events you want featured in the newsletter.